Docker Compose For Spring Boot with PostgreSQL
-
 Chinthaka Dinadasa
Chinthaka Dinadasa - 31 Dec, 2020

In this article, I’ll explain how we can set up a deployment using docker-compose for a Spring Boot application that uses a PostgreSQL database.
Technology stack which going to use in this tutorial,
- Spring Boot 3.0.3
- Spring Data JPA
- PostgreSQL – 11.4
- Lombok
- Docker – version 19.03.14
- Docker-Compose – version 1.27.4
- IntellijIdea for IDE
Prerequisites,
You need to set up docker and docker-compose in your machine to go forward with this tutorial.
I’ve used the following well-written articles from DigitalOcean to set up both docker and docker-compose on my local setup.
Setting Up PostgreSQL Base Project
I’ve created a simple REST API using Spring Boot with PostgreSQL database usage. First download or clone from GitHub.
$ git clone https://github.com/javatodev/spring-boot-postgresql-project-base.git
Or else you can skip this step and try a docker-compose setup with your own spring boot application which uses the PostgreSQL database.
Setup Docker Image For Spring Boot Application
In this tutorial, our docker-compose setup uses two main services or components. Those are the Spring Boot application and PostgreSQL database.
PostgreSQL is already available as a docker image from docker hub. You can just go and select the version you need from there.
But your project is still not pushed or published as a docker image. Hence first you need to have docker image for your spring boot application. Then you can use both images with docker-compose.
If you don’t have a good understanding of how to use docker with a spring boot application, you can refer our article on How to Dockerize Spring Boot Application.
Ok Let’s start the docker image creation,
First, create a file naming as Dockerfile in your project root folder. Then copy the following content into that file.
FROM openjdk:17-jdk-slim
LABEL maintainer="author@javatodev.com"
VOLUME /main-app
ADD build/libs/spring-boot-postgresql-project-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar app.jar
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "-Dspring.profiles.active=dev", "/app.jar"]
Now you have two ways of building docker compose setup.
-
Pointing Dockerfile into the docker-compose setup.
-
Giving created docker image to the docker-compose setup.
Let’s go forward with pointing docker file way, since giving docker image part will cover with postgreSQL image in this same setup.
Docker Compose File With Spring Boot and PostgreSQL
Now our application has the instruction to building the Docker image. So let’s create the docker-compose.yml file which allows us to combine Spring Boot application and PostgreSQL database in this setup.
First, go to the project root and create a file named docker-compose.yml
spring-boot-project-with-docker-compose-file
Using links to Build Communication Between Services.
There are two ways of building communication between spring boot application and the PostgreSQL database**. You can use one from the following two methods to build this docker-compose setup**.
I’ll start with using links to build communication between both. So add the following content into the docker-compose.yml file,
version: "3.7"
services:
api_service:
build: .
restart: always
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- postgresql_db
links:
- postgresql_db:postgresql_db
postgresql_db:
image: "postgres:15-alpine3.17"
restart: always
ports:
- "5433:5432"
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: java_to_dev_app_db
POSTGRES_USER: java_to_dev
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: nE5kMc7JCGNqwDQM
Here we have out two main services as,
-
api_service – Spring Boot REST API which runs on port 8080.
-
postgresql_db – PostgreSQL DB which runs on port 5432
Explanation about the configurations I have used in this docker-compose file,
build – Here we should introduce the image name to build under that service, Here we have our Dockerfile which developed for the API in the same level with docker-compose.yml so using “.” it will capture that docker file and build the handle the api_service when executing this file.
Additionally we have introduced postgres:11.4 as the docker image for postgreSQL DB. It will download from docker registry and start when needed.
More to research: We can do the same to spring boot API docker image as well, Just push that image to docker-hub and you can directly use given image name and version for this setup as well.
restart – always Always restart the container if it stops. If it is manually stopped, it is restarted only when Docker daemon restarts or the container itself is manually restarted.
ports – Here we are mapping local machine port along with port inside a docker container.
links – Here we are setting a link with postres_db service. So we can use database when defining ip address for database connection on our spring boot application. Then it will connects with the database running with this docker-compose.
environment – In this section we are setting the PostgreSQL database and postgres user password for this specific postgreSQL instance.
All done, Now let’s change our application.properties to support this database and application server setup.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://postgresql_db/java_to_dev_app_db
spring.datasource.username=java_to_dev
spring.datasource.password=nE5kMc7JCGNqwDQM
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization=true
spring.sql.init.mode=always
Here as you can see we are using that link value we used in docker-compose definition for host/IP address. additionally, password and DB has changed accordingly.
Using Depends On to Build Communication Between Services
The docker compose documentation specifies that links is deprecated and should be replaced with depends_on.
So here I’m setting the same docker-compose setup with using depends_on flag.
Just add following into the docker-compose.yml
version: "3.7"
services:
api_service:
build: .
restart: always
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- postgresql_db
links:
- postgresql_db:postgresql_db
postgresql_db:
image: "postgres:15-alpine3.17"
restart: always
ports:
- "5433:5432"
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: java_to_dev_app_db
POSTGRES_USER: java_to_dev
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: nE5kMc7JCGNqwDQM
Here we are using depends_on to set dependent services to api_service. So internally docker-compose will start dependency services first and it will start dependent service in the end. So basically here it will start the DB first and finally application will be started.
Additionally we have a small change on database connection properties, Here you should add service name for the host or IP on that database connection.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://mysql_db:3306/java_to_dev_app_db
spring.datasource.username=java_to_dev
spring.datasource.password=nE5kMc7JCGNqwDQM
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.datasource.initialization-mode=always
Running Spring Boot Application and PostgreSQL Database Using Docker Compose
Now we have our docker compose setup for this application. So first create a jar build for this application using following command,
Navigate to application root folder and execute,
$ ./gradlew clean build
Now there should be a newly created jar file with all the necessary files to run this application on build/libs folder.
Then create the build with docker compose to build docker image using built jar file.
$ docker-compose build
Then use following command to run whole setup using docker compose.
$ docker-compose up
Then It will capture the docker-compose.yml and start running using the instructions given on that file.
sample output:
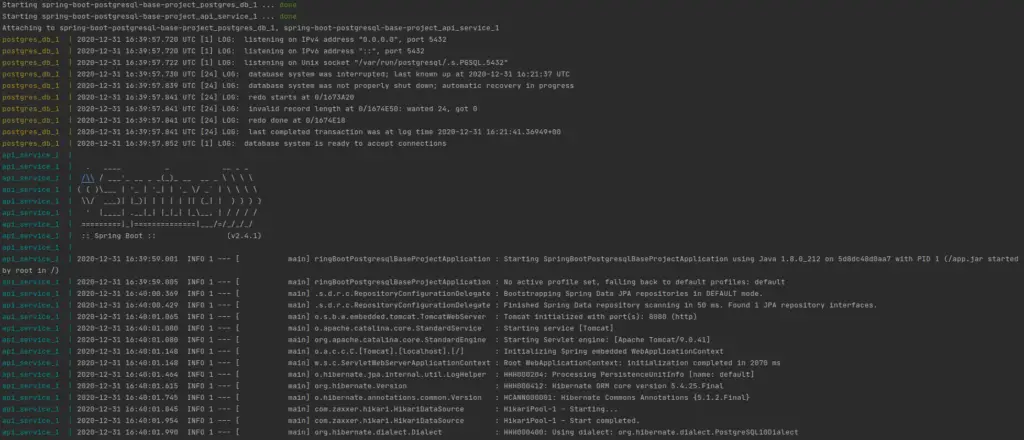
docker compose up sample output
Conclusion
Thanks for reading our latest article on Docker Compose Spring Boot with PostgreSQL with practical usage. I hope you got a good understanding of how we can use docker, docker-compose with spring boot application development and deployment.
If you are looking for spring boot based practical application development tutorials, just check our article series and comment on whatever new things you need to see on our website.
You can get docker-compose.yml and Dockerfile from GitHub gists.
Related Articles,